Odoo is a powerful ERP system that supports a wide range of functions. From managing CRM , Inventory to create Sales and accounting documents. Due to the diverse functionalities, Odoo organizes these features in different apps.
That mean you'll need to set access permissions for specific apps, documents, and data for users in different departments by using Access Rights and Record Rules to manage these permissions.

Designed by Freepik.com
First, you need to understand Models, by going to Settings > Menu Items > and selecting the Menu you want to view. Normally, the visibility tab is left blank, meaning the model is visible to all User Groups (which have their own Access Rights and Record Rules). I'll not recommend to adjusting the visibility settings for any model, leave it blank, and we will manage everything with access rights instead.
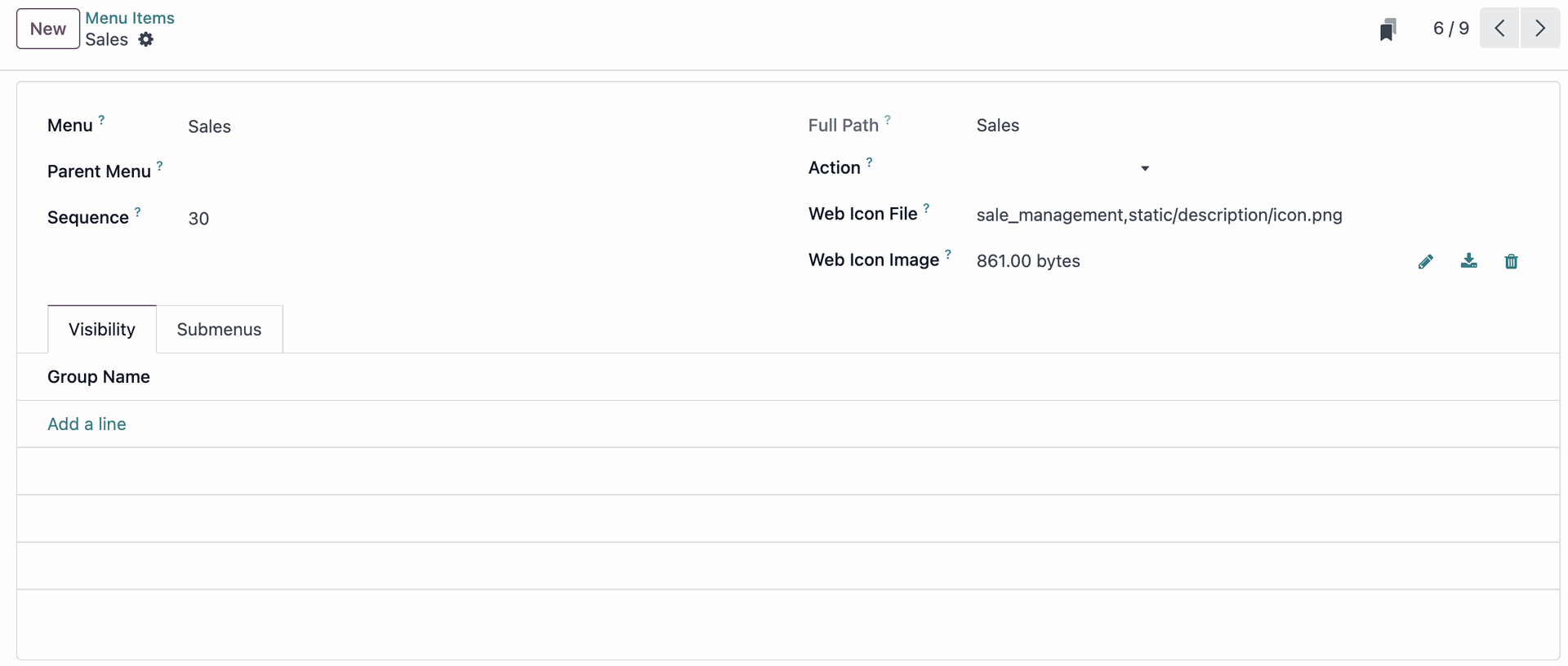
What are Access Rights ?
Access Rights define what users are allowed to do, such as 'Read' documents without the ability to 'Write' and it's work alongside models.
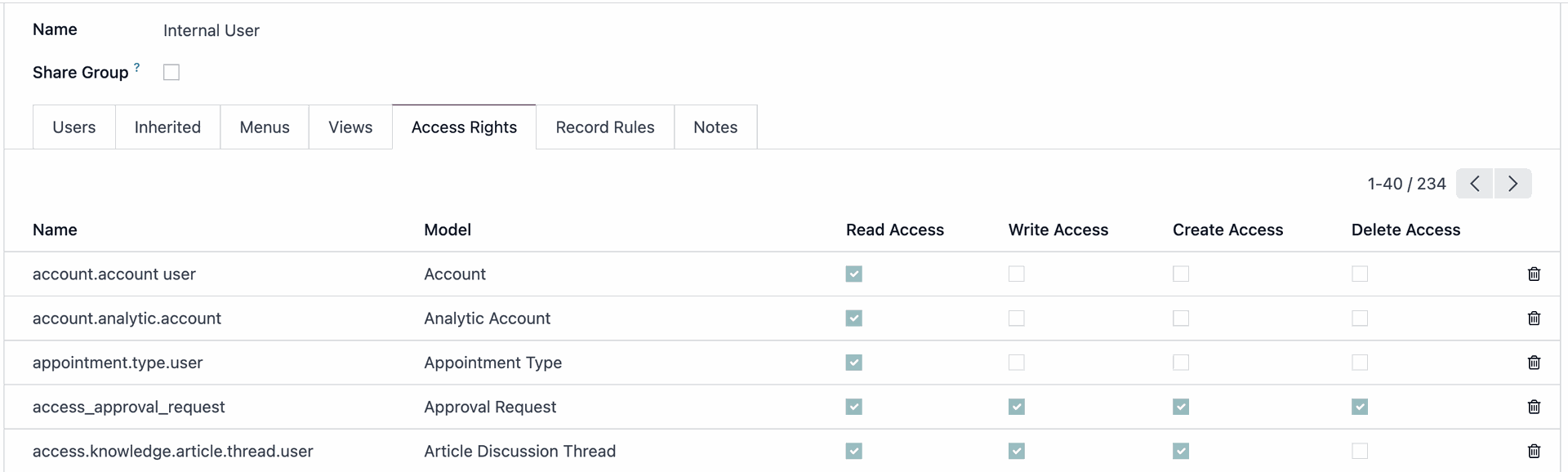
You can check which Model a document belongs to by going to Debug Mode > Bug Icon > View Access Rights. This will show the Model name and which user groups have access to the document.
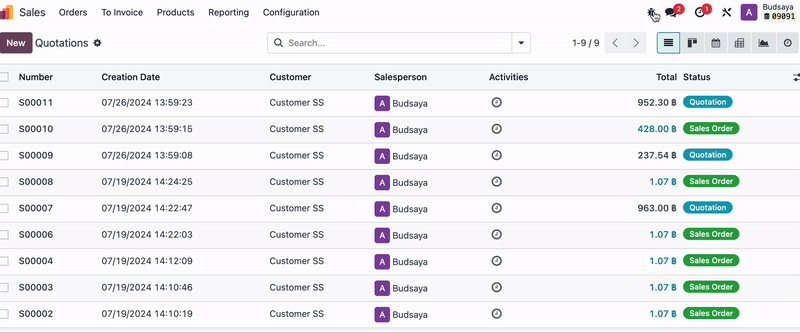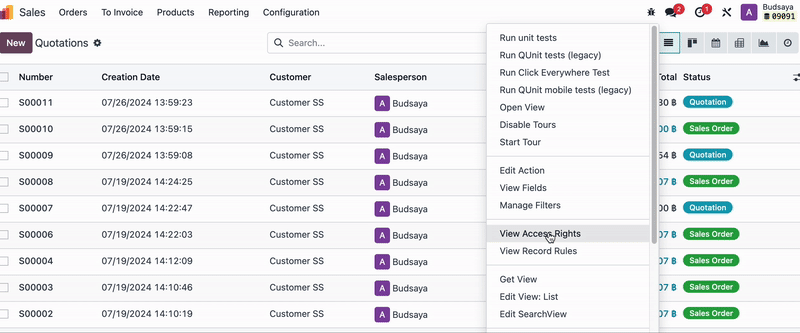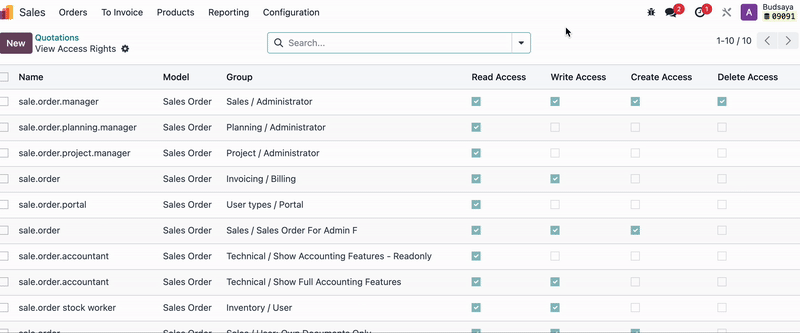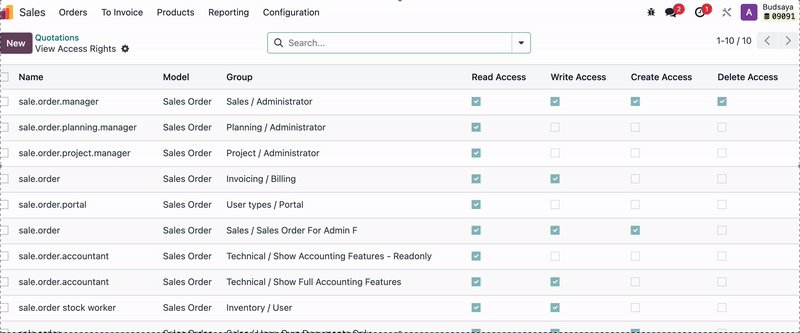
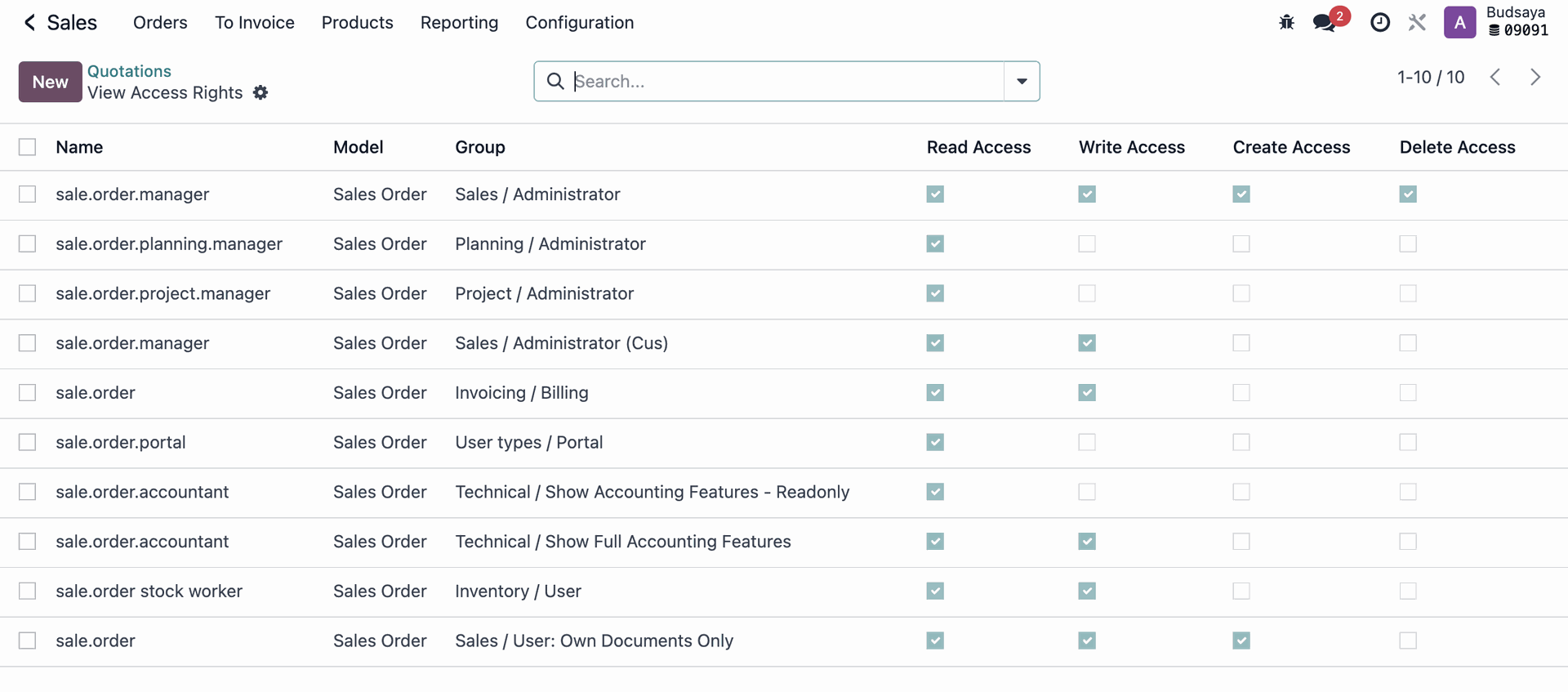
For example, if you don’t want Employee A, who is in HR, to see the ‘Sales Apps’:

You can adjust settings by going to Sales Apps, then checking which Model the Sales documents are under and which user groups have Access Rights.
In this case, 'Admin A' belongs to the ‘Sales / Administrator’ and ‘Sales / Users: Own Documents Only’.
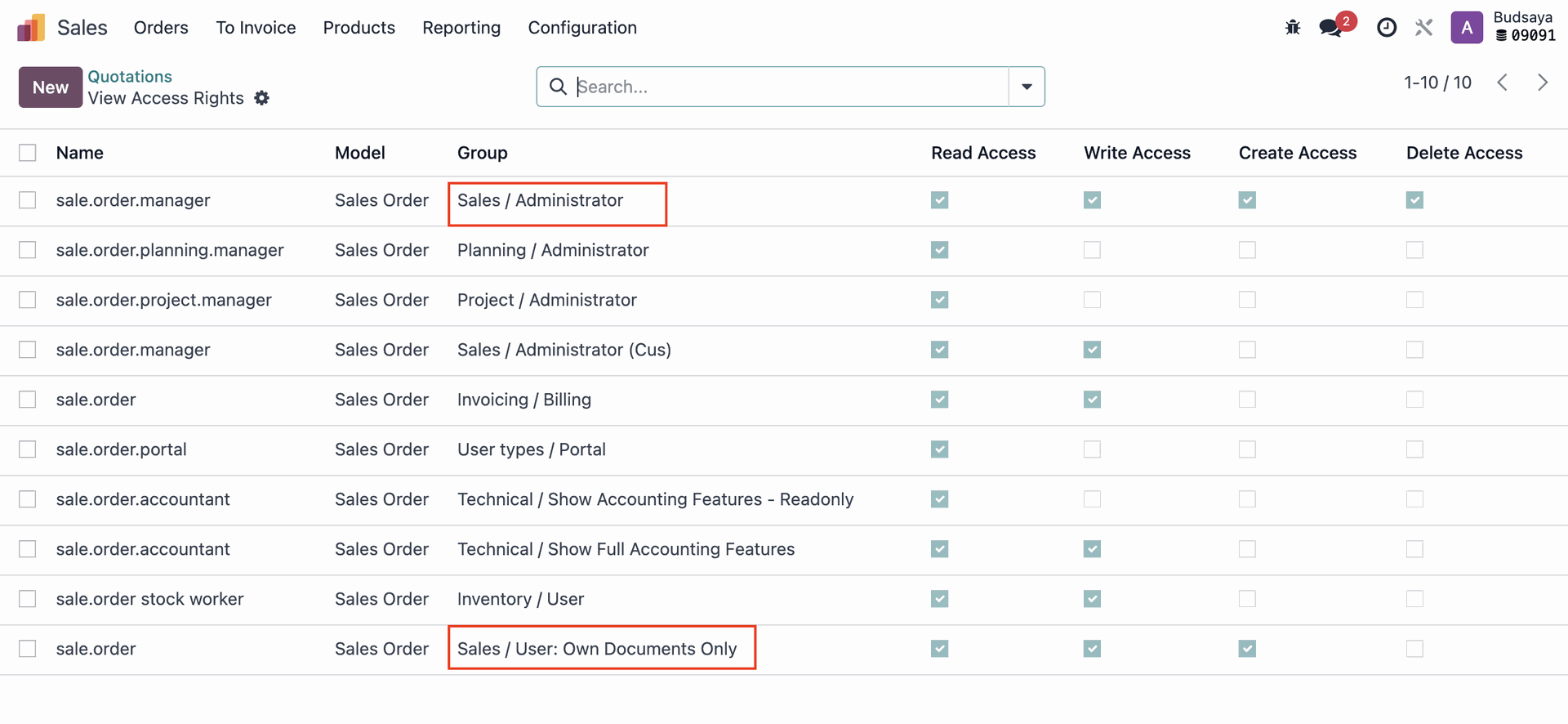
As mentioned, we don’t recommend adjusting model visibility, You should remove 'Admin A' from the user groups with Access Rights ‘Sales / Administrator’ and ‘Sales / Users: Own Documents Only.’
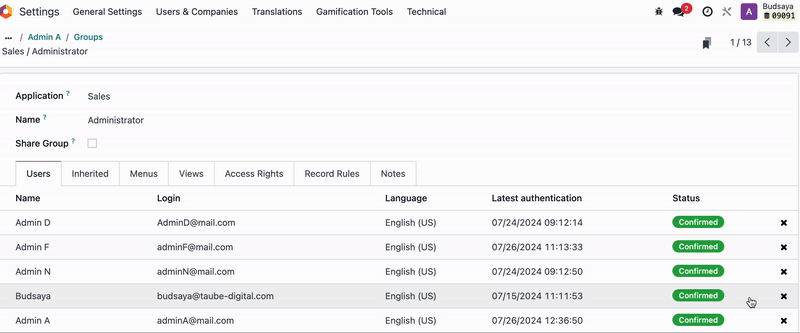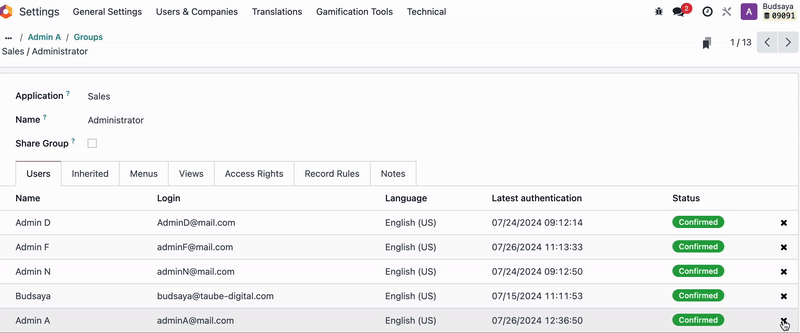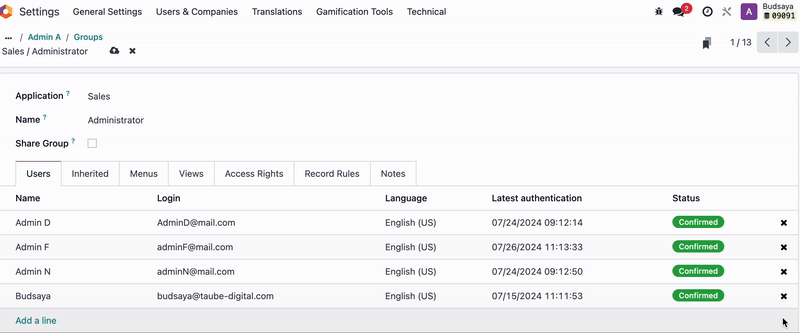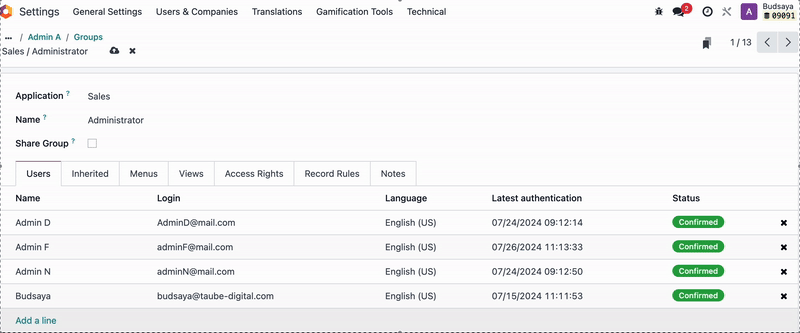
Admin A will find that the Sales App is no longer visible in the menu upon login.

What are Record Rules ?
Record Rules are used to set conditions within a Model to control access based on specific condition.
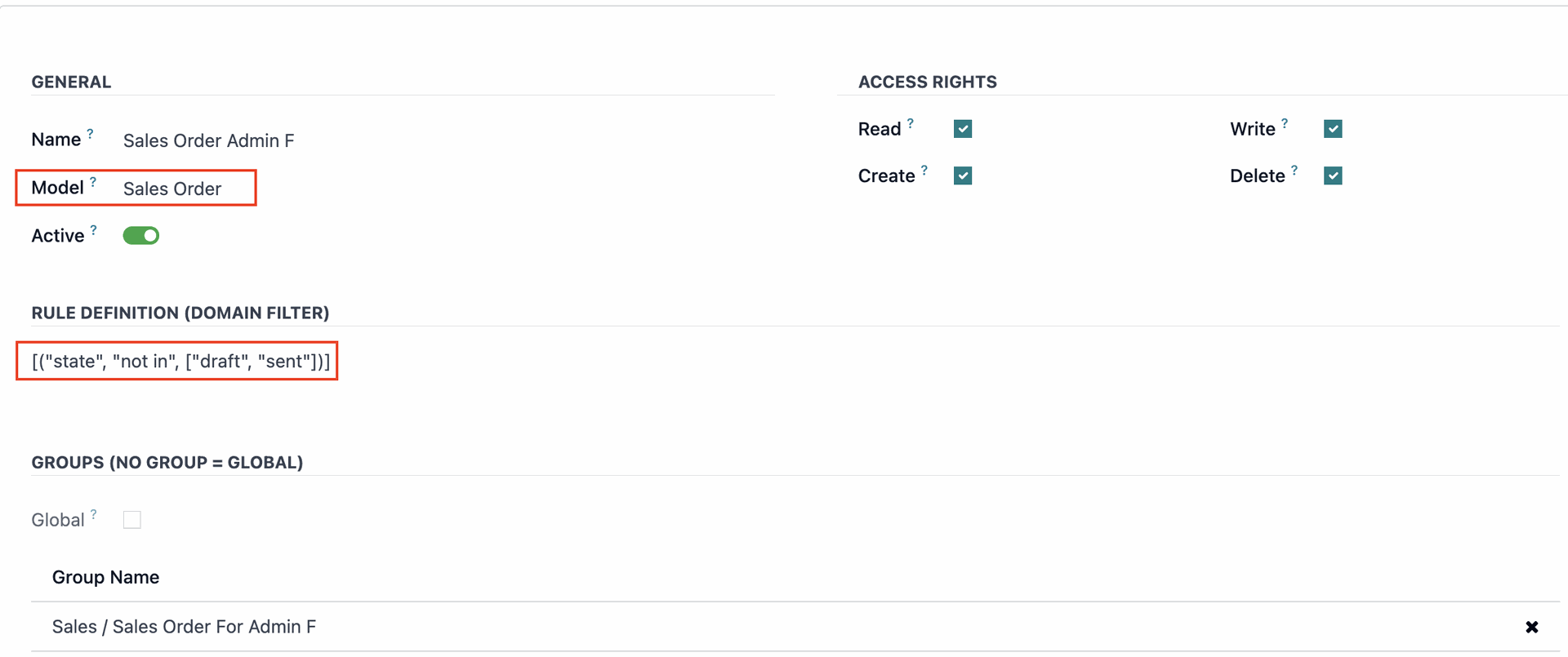
For example, if you don’t want Employee F, who is in the warehouse, to see unconfirmed Quotations (Sales Orders):
Do the similar steps to check which Model the unconfirmed Quotations (Sales Orders) belong to and which user groups have 'Record Rules' for this document.
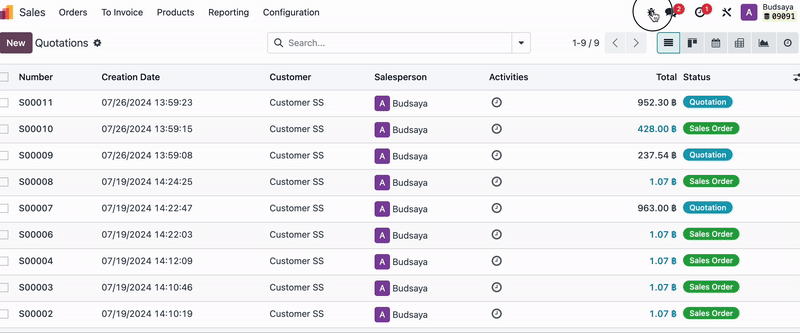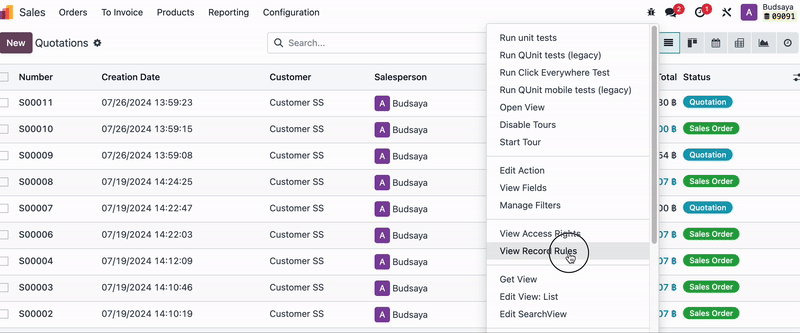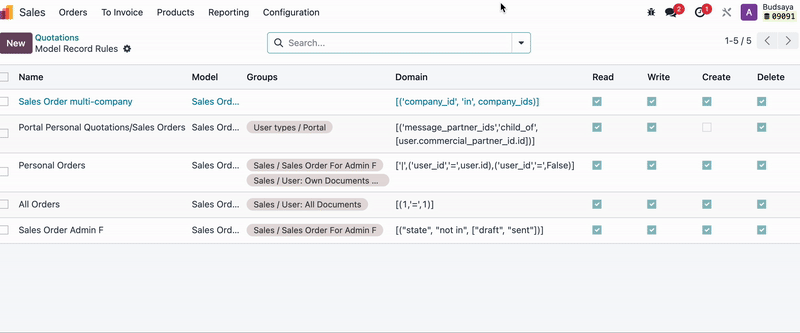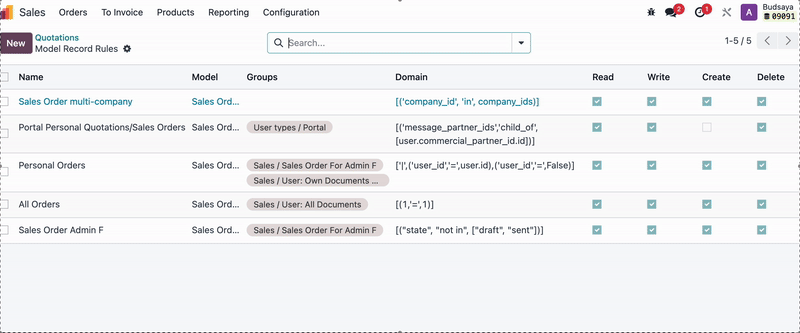
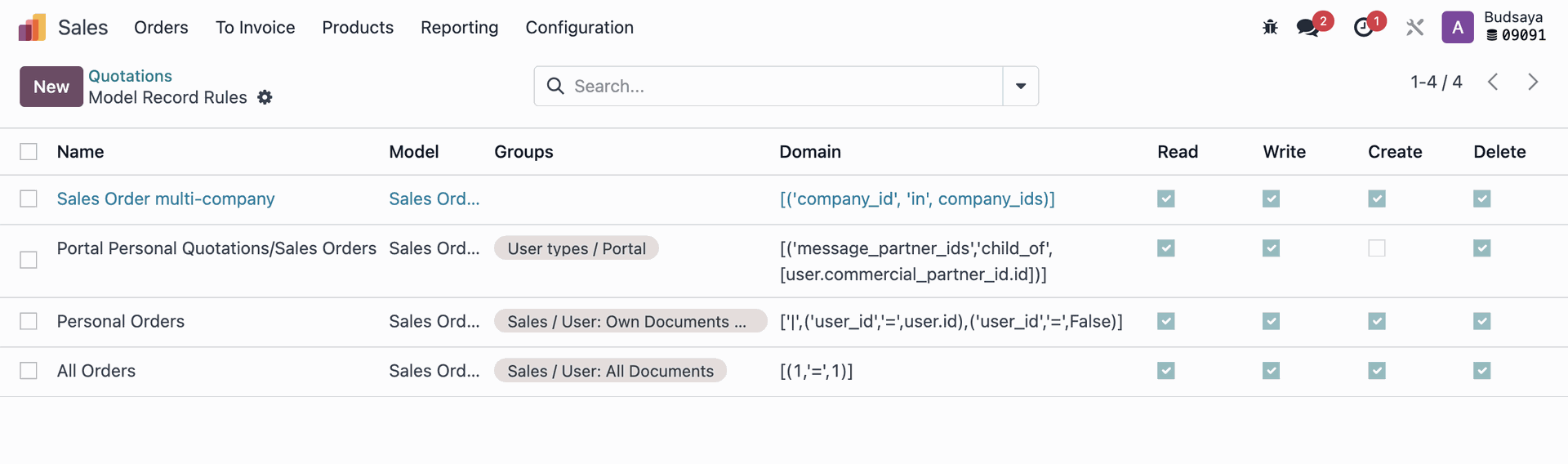
Then, go to the User Groups, remove 'Admin F' from the User Group, and create a duplicate of that User Group.
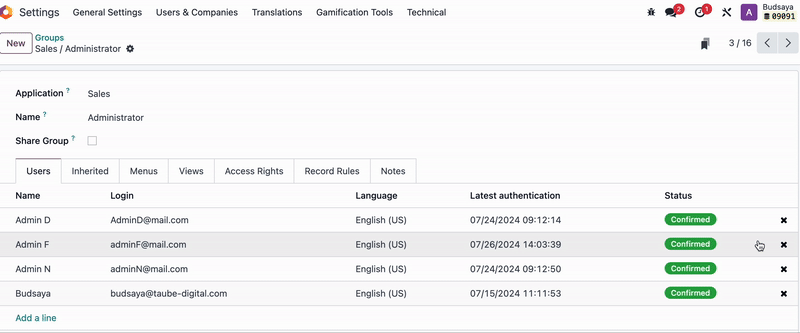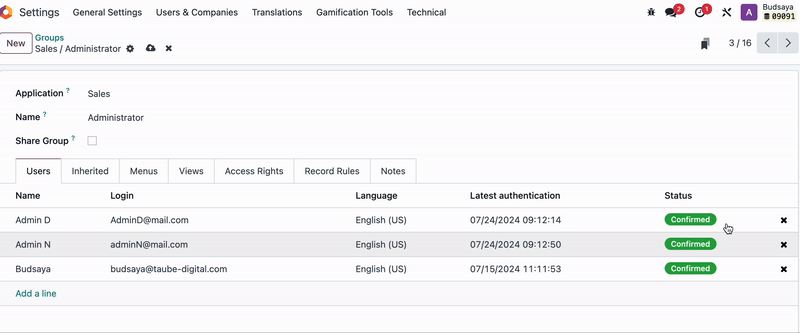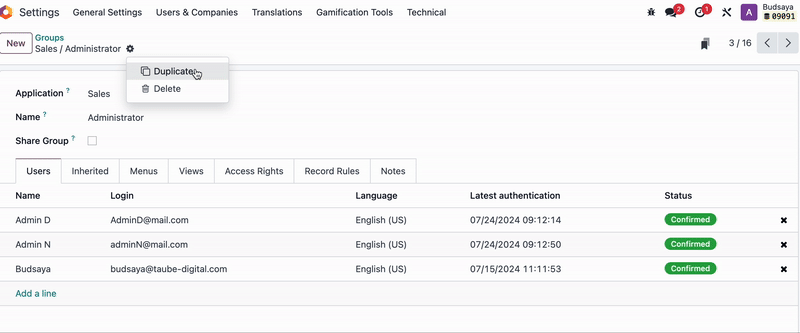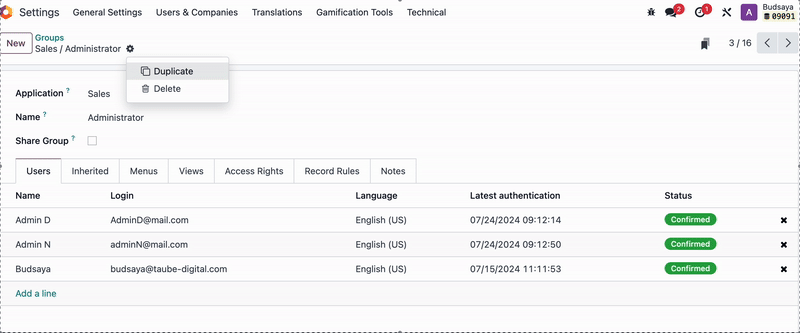
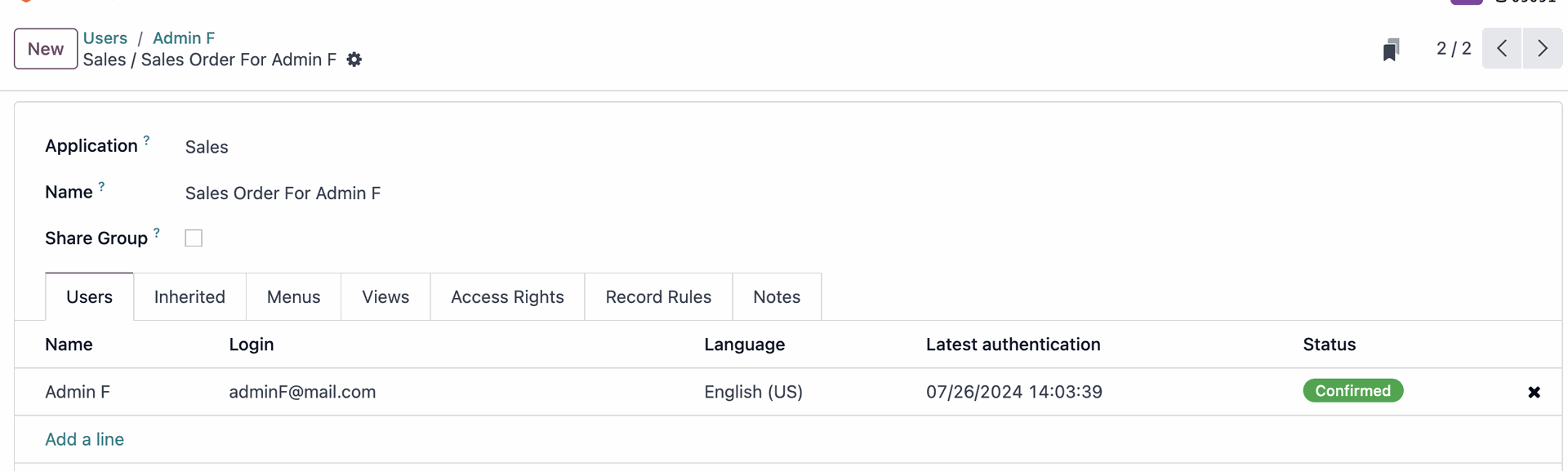
Add 'Admin F' and setting name of new user Group, and remove other users from this group.
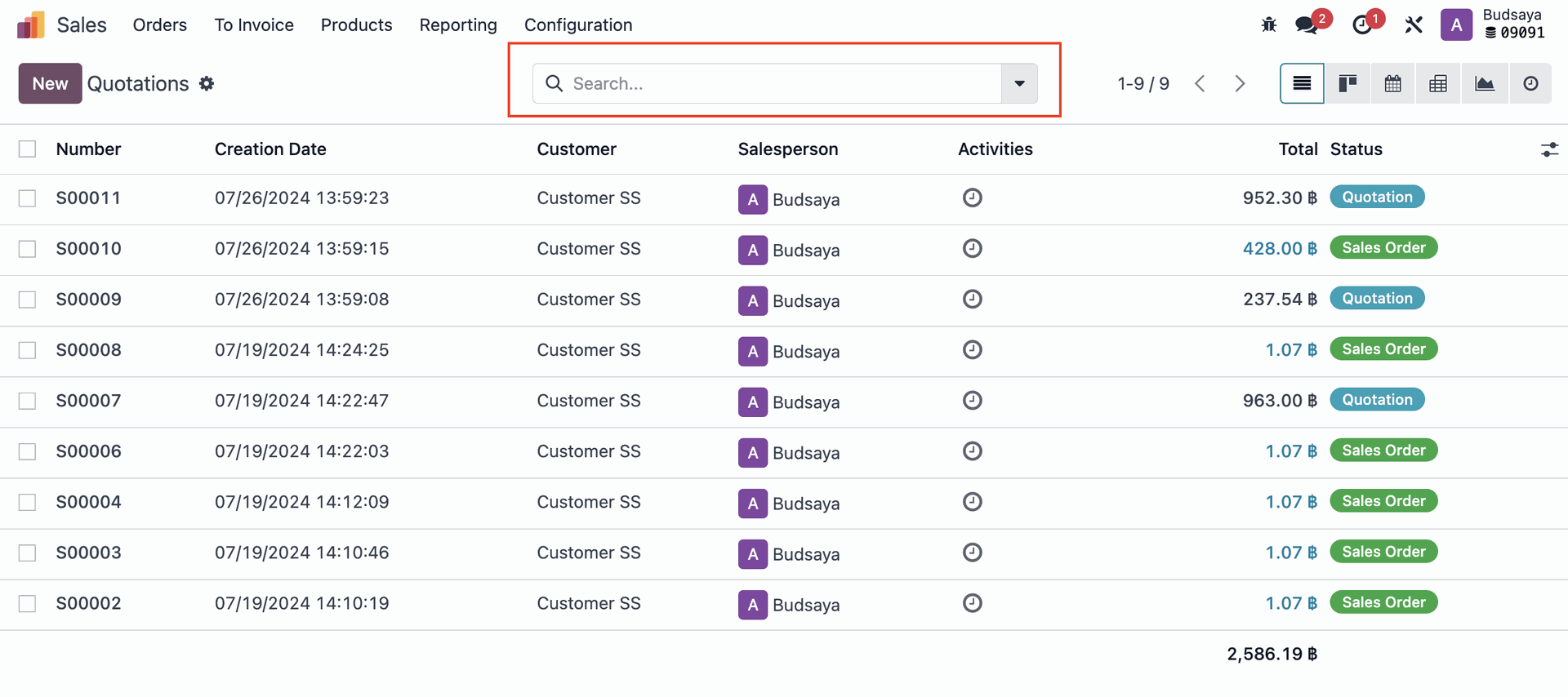
Go to ‘Sales App’ > ‘Quotations’ and set a filter to show only confirmed quotations.
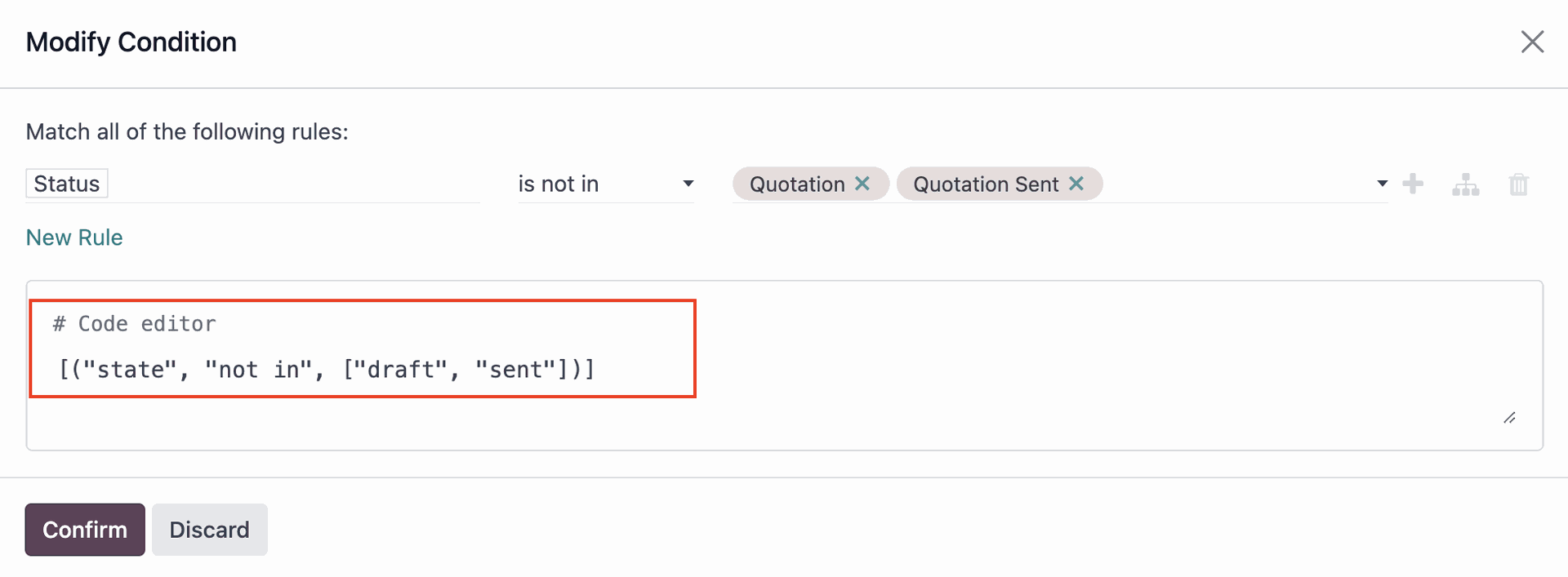
Copy the condition and go to Settings > Conditions > Record Rules, then select the Model of the document (Sales Order). Then, paste the conditions from the filter you set earlier, and in the 'Group Name' specify the new User Group you created for 'Admin F'.
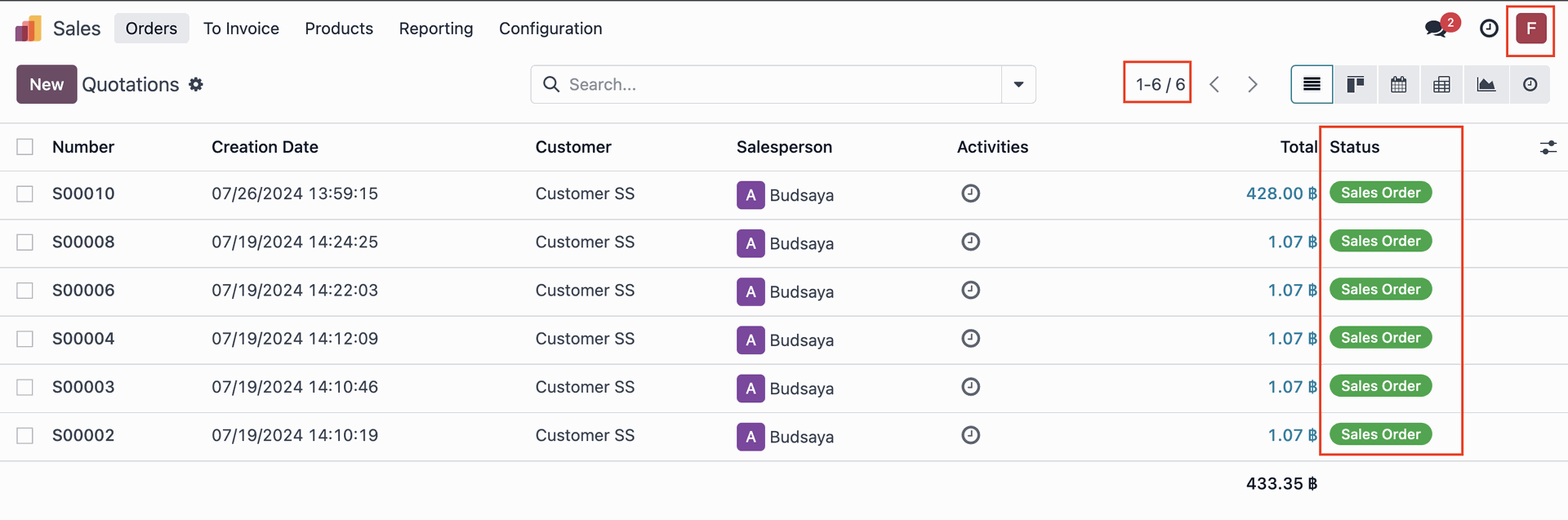
When 'Admin F' logs in, they will only see Quotations that are confirmed as Sales Orders.
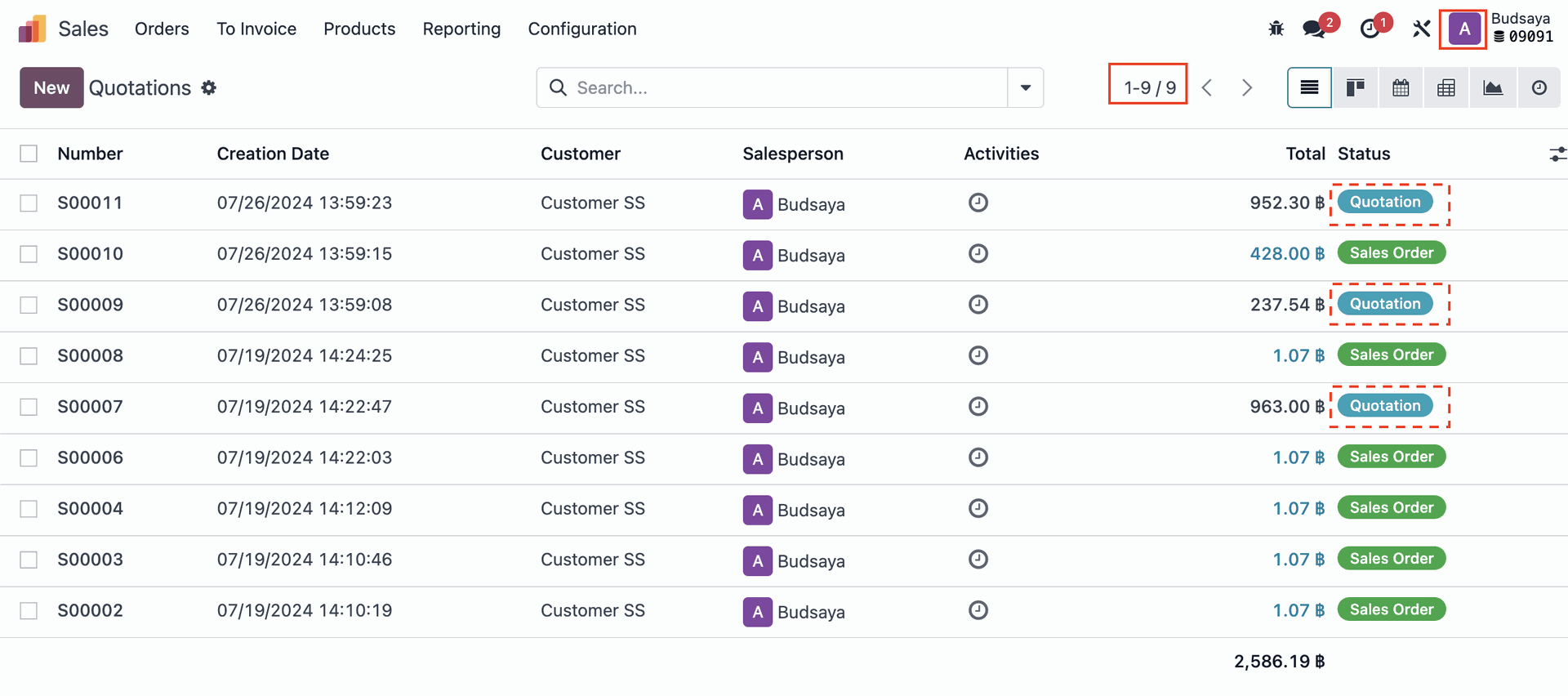
This is just a basic example. Access Rights and Record Rules can be configured with more complexity. And If you have complex requirements, a good implementer will inform you about certain conditions that may need configuration. For example, if you want Admin A to be unable to see inventory levels in Warehouse B but still be able to pick items from it, we will ask you to confirm this. In reality, if Admin A cannot see the remaining stock, how will they pick the items? Or do you want them to pick items regardless of the stock levels?
You can contact us for advice on setting user permissions, regardless of the specific case, Our team has experience working with Odoo’s headquarters in Belgium. We include both Thai and international members, with expertise in implementing user permissions at both basic and advanced levels in factory settings.



